The Science Behind Zero Gravity Beds and Sleep Health
Written by Nectar Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by Nectar Editorial Team
Last Updated on Jul 25, 2025
In this Article:
Throughout history, beds have evolved from primitive ground coverings to sophisticated, smart mattresses. With more and more innovation being done in the field, it’s always exciting to see how humanity’s unchanging need for rest is improved by our technological capabilities.
Zero gravity is certainly one of these innovations, going beyond traditional beds and offering remarkable benefits. This guide explains what zero gravity beds are, how they work, and the various benefits they provide.
The Origins and Concept of Zero Gravity
The concept of zero gravity beds is rooted in space science. NASA developed the zero gravity position to reduce the gravitational stress astronauts face during space missions. This position reduces tension and helps distribute pressure more evenly – so it’s no surprise that it was swiftly adopted into sleep technology. How does it work? By balancing weight distribution, minimizing strain on your spine and joints.

How Zero Gravity Beds Work
Zero gravity beds operate with advanced mechanics – the key feature being the adjustable bed frame, which tilts and raises different parts of the bed. With an adjustable bed frame, it is possible to replicate the zero gravity position, thereby reaping the health benefits.
The adjustable frame allows independent movement of the head and feet to help users find their ideal sleeping posture. It also enables specific adjustments for various health needs, such as potentially reducing back pain or improving circulation[1,2].
Technology plays a significant role in this level of functionality. Many zero gravity beds offer remote controls and even smartphone apps to easily adjust your positioning. Some models even include additional features – like massage functions or USB ports – to enhance their user experience. But most importantly, zero gravity beds emphasize ergonomics and comfort, catering to a wide range of user preferences.
What is a Zero Gravity Bed?
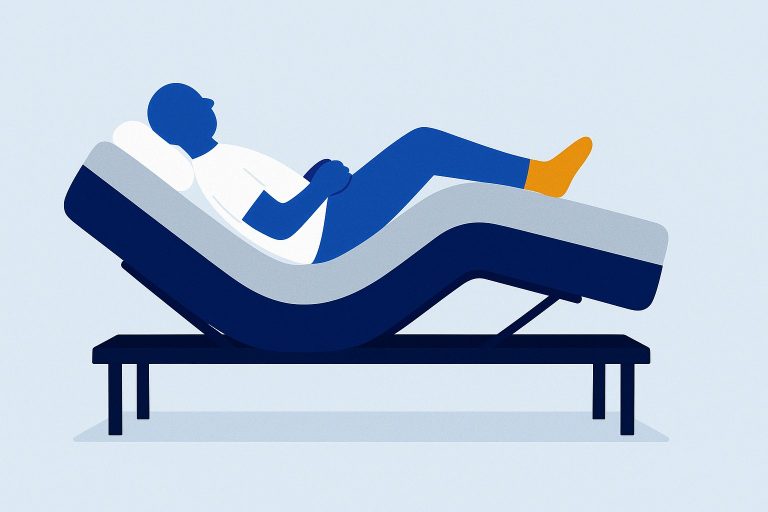
A zero gravity bed is an adjustable bed with a setting that mimics the position astronauts assume during rocket launches to minimize stress on their bodies. By elevating both the head and legs slightly above the torso, zero gravity beds reduce pressure points, enhance circulation, and alleviate body tension.
The primary feature of a zero gravity bed is its adjustability. It offers an ergonomic position that elevates both the head and feet slightly above the heart level, simulating a weightlessness effect that reduces pressure on key areas of the body. This strategic positioning helps improve circulation and relieves tension throughout the body.
Unlike traditional beds, a zero gravity bed distributes weight evenly across the sleeping surface, extending its benefits beyond mere comfort to deliver significant health advantages. The adjustable nature of these beds allows users to find their optimal position for both relaxation and sleep.
Benefits of Memory Foam and Gel-Infused Foam
Health Benefits of Zero Gravity Beds
Zero gravity beds offer a range of health advantages, especially when compared to standard mattresses. They have been consistently researched, with one study showing that even a small adjustment in head-of-bed elevation was associated with a 32% reduction in the severity of obstructive sleep apnea[3].
Below are some of the ways a zero gravity bed can help improve sleep health:
1. Alleviating Back Pain and Improving Spinal Alignment
By elevating the head and legs slightly above the torso, zero gravity beds may reduce pressure points, enhance circulation, and alleviate body tension. Most back pain during sleep results from poor posture and uneven weight distribution. By providing support at multiple pressure points, zero gravity beds promote optimal spinal alignment – which can help reduce back pain[4,5].
2. Enhancing Blood Circulation and Reducing Swelling
Zero gravity beds enhance blood circulation by elevating the legs above heart level. This positioning can help reduce swelling and edema[6]. It also allows gravity to aid blood flow back to the heart more efficiently.
Improved circulation supports cardiovascular health and can be beneficial for those with varicose veins[7]. By facilitating blood flow, zero gravity beds can help users wake up feeling more refreshed. Reduced swelling also contributes to decreased joint pain, enhancing overall mobility.
The specific angle of zero gravity elevation can also promote heart health. This can be particularly beneficial for those with circulatory issues or those who spend long periods on their feet[8].
3. Preventing Discomfort During Sleep
For individuals with acid reflux, elevation of the head can help keep airways open and reduce the backflow of gastric acid, preventing discomfort during sleep[9].
- Improved Airway Alignment and Breathing:
Elevating the head in the zero gravity position aligns airways better, making it easier to breathe throughout the night. This elevation prevents the tongue and soft tissues in the throat from collapsing back into the airways – a common cause of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea[10]. By maintaining an open airway, zero gravity beds can help ensure a more consistent and uninterrupted airflow during sleep. - Alleviation of Acid Reflux and GERD:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and acid reflux can cause considerable discomfort and disrupt sleep. The zero gravity position helps by keeping the head elevated above the stomach, reducing the likelihood of acid flowing back into the esophagus[11]. This not only helps minimize acid reflux episodes but also reduces the potential for the acid to cause throat irritation, which can further exacerbate snoring and discomfort. - Reduction in Congestion and Sinus Pressure:
For individuals who experience nighttime congestion or sinus issues, the zero gravity position can help by improving drainage and reducing pressure[12]. Elevation prevents mucus from pooling in the sinuses and promotes better sinus drainage, which can alleviate congestion and reduce the pressure that often leads to sinus headaches.
The Role of Adjustable Bed Frames in Zero Gravity Beds
Adjustable bed frames are a foundational component in the functionality of zero gravity beds. The importance of adjustable bed frames lies in their ability to accommodate personal preferences. Some frames, including Nectar’s adjustable base options, offer additional customization features, such as programmable positions for reading, watching TV, or the zero gravity position.
How to Adjust the Frame to Zero Gravity Position
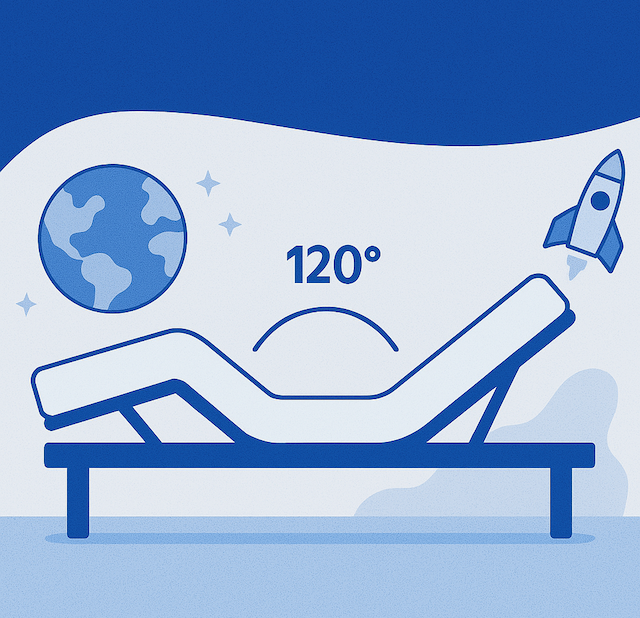
The adjustable bed frame’s versatility allows users to experiment with different angles to achieve their ideal zero gravity position, which mimics the body’s posture in a weightless environment. To properly adjust the bed to this position:
- Elevate both the head and knees so they are slightly above the heart level
- This setup should position the torso and legs to form roughly a 120-degree angle with each other
- This specific angle helps maintain spinal alignment, reducing strain on the neck and shoulders
Tip: It’s important to fine-tune these adjustments according to personal comfort and preferences, as some might prefer a higher leg elevation after a long day.
How to Adjust the Frame to Zero Gravity Position
The adjustable bed frame’s versatility allows users to experiment with different angles to achieve their ideal zero gravity position, which mimics the body’s posture in a weightless environment. To properly adjust the bed to this position:
- Elevate both the head and knees so they are slightly above the heart level
- This setup should position the torso and legs to form roughly a 120-degree angle with each other
- This specific angle helps maintain spinal alignment, reducing strain on the neck and shoulders
Tip: It’s important to fine-tune these adjustments according to personal comfort and preferences, as some might prefer a higher leg elevation after a long day.

Choosing the Right Mattress for an Adjustable Bed Frame
Finding the perfect mattress for your zero gravity bed comes down to a few key factors: the mattress type, how well it flexes with your adjustable base, its thickness, firmness level, and comfort features. Keep these points in mind while shopping to ensure you get the most from your adjustable bed experience.
Mattress Types Compatible with Adjustable Beds
- Memory Foam: Memory foam is highly recommended for zero gravity beds thanks to its flexible, contouring properties. It adapts to the shape of the body while responding well to the bed’s adjustments, maintaining comfort and support as your bed frame moves. Memory foam also helps in reducing pressure points and supporting proper spinal alignment.
- Latex: Latex mattresses are another excellent option for zero gravity beds. They offer a similar contouring effect to memory foam but with more bounce, which some people prefer for easier movement in bed. Latex is also durable and resistant to sagging, making it ideal for adjustable beds.
- Hybrid: Hybrid mattresses combine the best features of innerspring and foam or latex layers. They provide the firm support of springs with the comfort of foam or latex top layers. Hybrids are a good choice for zero gravity beds as they offer good flexibility and adaptability when it comes to adjusting the bed frame.
Why Traditional Innerspring Mattresses Don’t Work Well
Traditional innerspring mattresses are built using interconnected coil systems that resist bending, much like trying to fold a wire mesh. When forced to bend with an adjustable base, these mattresses face several issues:
- Resistance to Flexibility: The rigid coil structure fights against the bed’s adjustments, creating strain on both the mattress and bed mechanism.
- Structural Damage Risk: Repeated bending can weaken and eventually damage the coil system, similar to how repeatedly bending a metal wire eventually causes it to break.
- Comfort Issues: Rather than conforming to your body in the zero gravity position, a bent innerspring mattress often creates uncomfortable pressure points and uneven support.
- Warranty Concerns: Many innerspring mattress warranties explicitly exclude coverage when used with adjustable bases.
For adjustable beds, look instead for specifically compatible options like memory foam, latex, or hybrids with individually-wrapped coils that can flex with the bed’s movements.
Additional Mattress Features to Consider
Mattress Flexibility and Durability
The mattress you choose must be flexible enough to move with the adjustments of the bed frame without compromising its structural integrity. It should also be durable enough to withstand repeated movements over time. Check for mattresses specifically designed for use with adjustable beds.
1. Thickness and Firmness
A mattress that is too thick may not flex as easily with the bed’s adjustments. Typically, a mattress thickness of 12-15 inches works best with adjustable beds, providing enough cushioning while maintaining flexibility.
The ideal firmness will depend on your personal preference and specific health needs. However, a medium-firm mattress often offers a good balance of support and comfort for various sleeping positions and is conducive to the zero gravity posture.
2. Layer Construction
Look at the construction of the mattress layers. Ideally, the top comfort layer should be soft enough to offer immediate relief and comfort, while the underlying support layers provide the firmness necessary for body support. This layered construction helps accommodate the bends of the adjustable bed while maintaining the overall integrity and comfort of the mattress.
3. Trial Period and Warranties
Given the investment in a zero gravity bed and mattress, look for manufacturers that offer a trial period, allowing you to test the mattress with your adjustable bed frame to ensure it meets your needs.
How to Adjust the Frame to Zero Gravity Position
The adjustable bed frame’s versatility allows users to experiment with different angles to achieve their ideal zero gravity position, which mimics the body’s posture in a weightless environment. To properly adjust the bed to this position:
- Elevate both the head and knees so they are slightly above the heart level
- This setup should position the torso and legs to form roughly a 120-degree angle with each other
- This specific angle helps maintain spinal alignment, reducing strain on the neck and shoulders
Tip: It’s important to fine-tune these adjustments according to personal comfort and preferences, as some might prefer a higher leg elevation after a long day.
Achieving Restorative Sleep with Zero Gravity Beds
Embracing zero gravity technology can lead to better sleep, less pain, and improved overall well-being. This guide has explored how these innovative beds work, the health benefits they provide, and how to choose the right adjustable frame and mattress for you.
If you’re in search of sleep systems designed for zero gravity sleep, explore Nectar’s adjustable bed frame options and discover our exclusive mattress and adjustable base bundles. Our adjustable beds are compatible with Nectar bed frames, so you can enjoy the benefits of zero gravity sleep without sacrificing on style.
This article is for informational purposes and should not replace advice from your doctor or other medical professional.
Citations
[1] Desouzart, G., Matos, R., Melo, F., & Filgueiras, E. (2016). Effects of sleeping position on back pain in physically active seniors: A controlled pilot study. Work, 53(2), 235-240.
[2] Ancuelle, V., Zamudio, R., Mendiola, A., Guillen, D., Ortiz, P. J., Tello, T., & Vizcarra, D. (2015). Effects of an adapted mattress in musculoskeletal pain and sleep quality in institutionalized elders. Sleep Science, 8(3), 115-120.
[3] Bignold, J. J., Deans-Costi, G., Goldsworthy, M. R., Robertson, C. A., McEvoy, D., Catcheside, P. G., & Mercer, J. D. (2017). Poor long-term patient compliance with the tennis ball technique for treating positional obstructive sleep apnea. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 13(8), 929-933.
[4] Ko, P. S., & Nelson, N. L. (2019). Comparison of sleep quality based on sleeping position in patients with chronic neck pain. Journal of Physical Therapy Science, 31(7), 542-546.
[5] Desouzart, G., Gagulic, S., & Ptak, M. (2016). Effects of sleep posture on back pain. Medicina Sportiva: Journal of Romanian Sports Medicine Society, 12(1), 2739-2744.
[6] Blättler, W., & Zimmet, S. E. (2008). Compression therapy in venous disease. Phlebology, 23(5), 203-205.
[7] Kahn, S. R., Shapiro, S., Wells, P. S., Rodger, M. A., Kovacs, M. J., Anderson, D. R., & Ginsberg, J. S. (2014). Compression stockings to prevent post-thrombotic syndrome: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet, 383(9920), 880-888.
[8] Weller, C. D., Buchbinder, R., & Johnston, R. V. (2016). Interventions for helping people adhere to compression treatments for venous leg ulceration. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (3).
[9] Khan, B. A., Sodhi, J. S., Zargar, S. A., Javid, G., Yattoo, G. N., Shah, A., … & Khan, M. A. (2012). Effect of bed head elevation during sleep in symptomatic patients of nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 27(6), 1078-1082.
[10] Souza, F. J. F. B. D., Genta, P. R., de Souza Filho, A. J., Wellman, A., & Lorenzi-Filho, G. (2017). The influence of head-of-bed elevation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep and Breathing, 21(4), 815-820.
[11] Ness-Jensen, E., Hveem, K., El-Serag, H., & Lagergren, J. (2016). Lifestyle intervention in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 14(2), 175-182.
[12] Li, H. Y., Lee, L. A., Kezirian, E. J., & Lin, Y. S. (2016). Incidence of revision surgery after minimally invasive transpalatal tongue-base surgery for obstructive sleep apnea. JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery, 142(4), 344-349.